Blockchain Technology Everything You Need to Know Crypto Universe
In recent years, the phenomenon that has attracted much attention is the term “blockchain”, which is mainly related to such cryptocurrencies as Bitcoin and Ethereum. However, the applicability of such blockchain security is not limited to cryptocurrencies; it has a great number of possibilities for changing the Finance and Supply Chain Management sectors. But what is this blockchain and why is it so radical? Now let’s get to the ground of this revolutionary technology.
What is Blockchain?
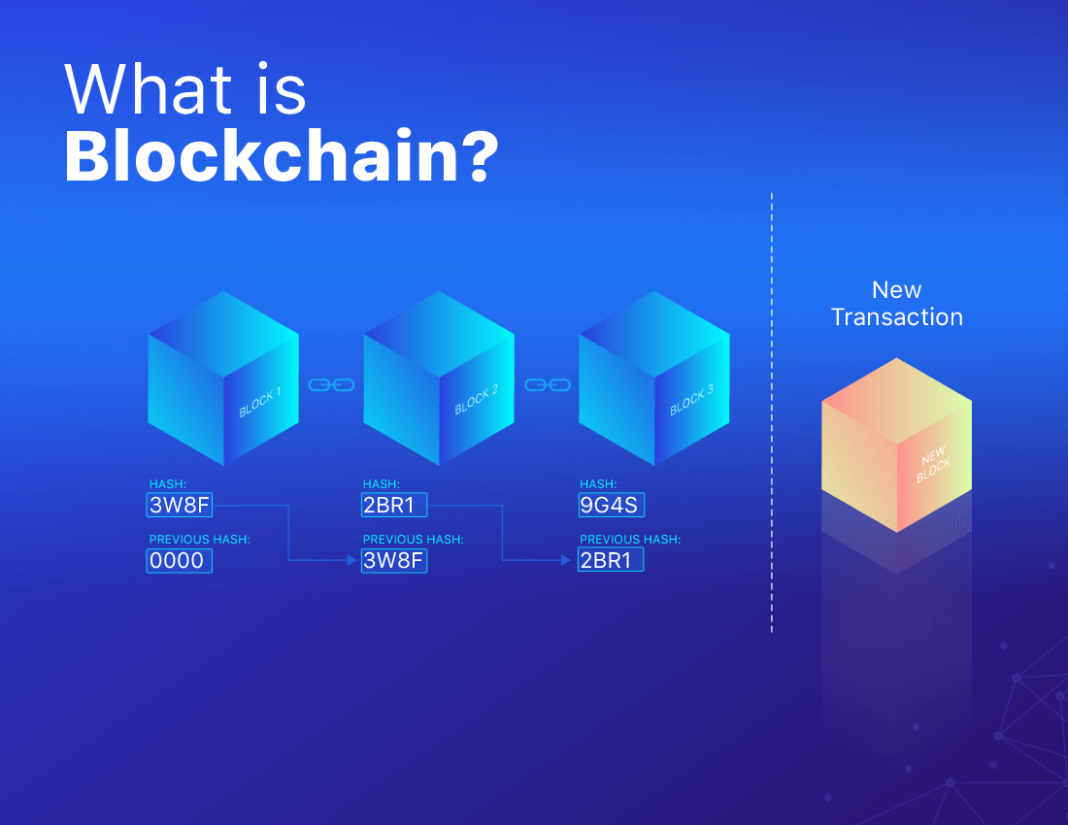
A blockchain is an open, distributed ledger that stores multiple transaction data over the internet that cannot be tampered with once stored. This technology advances such features as transparency, security, and the inability to tamper with the records making it a solid solution in a range of applications.
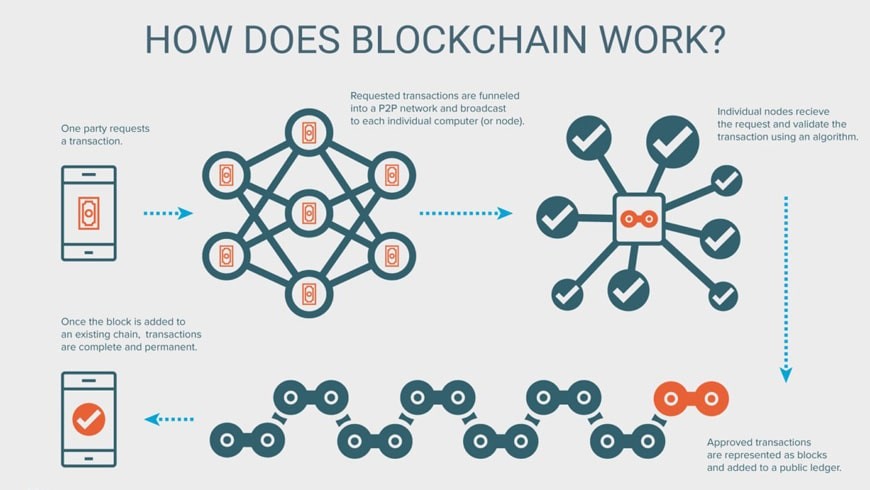
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how blockchain works:
Decentralization:
While traditional databases are managed on a centralized server where the authority of the data lies, in a blockchain, there are nodes which are computers containing a copy of the entire ledger. There was always a delegation of administrative functions to different centers to eliminate the possibility of one center or organization exerting too much influence and increasing security.
Blocks and Chains:
These involve the arrangement of any outgoing transactions locally into blocks comprising various kinds of transactions. Each block has a list of transactions and a pointer, known as hash or Hash Pointer, to the previous block creating a chain. This structure means that when a block is created, it cannot be altered without affecting other related blocks making the blockchain unalterable.
Consensus Mechanisms:
For the addition of a new block to the chain of the blocks, the nodes have to come to a consensus. There are many consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake: they guarantee that all the nodes in the system have the same vision of the transactions’ legitimacy, thus preserving the blockchain’s integrity.
Key Features of Blockchain
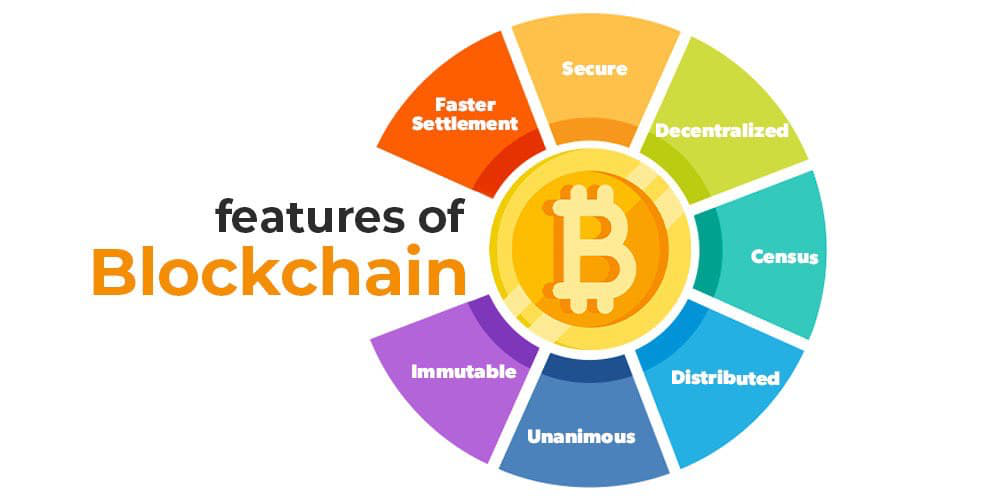
Immutability:
Data that is stored in a block cannot be changed or erased as it can be only added to the next block. This makes blockchain the unchangeable record of the truth which can be of great use in auditing and compliance.
Transparency:
All the activities performed on a public blockchain are shown to all the parties involved which reduces the possibility of a scam. It is also possible to make private blockchains, and in that case, all the participants can check the transactions and exercise control over them.
Security:
It is for this reason that blockchain is less vulnerable to hacking and fraud and is decentralized in its structure. Each is encrypted and connected to the other so that if data is altered [it is] almost impossible to go unnoticed.
Efficiency:
Blockchain reduces the time and expenses that are incurred while completing the same tasks through other models that contain several intermediate nodes. For instance in the financial sector, while using blockchain, one could be able to make cross-border payments faster and cheaper than is done by a bank.
Applications of Blockchain
Cryptocurrencies:
The best and familiar use of blockchain is in cryptocurrencies such as bitcoins and ethereum as they assist in the validation of transactions. Blockchain establishes secure and transparent means of recording and documenting transactions without any reference to the bank’s authorization.
Supply Chain Management:
Blockchain has the possibility of improving the track-and-trace processes of goods and supply chains. Thus the recording of every step of a product journey helps in the eradication of fraud, maintaining authenticity and efficiency.
Smart Contracts:
These are contracts that, in a way, execute themselves with the clauses and agreements coded in. Smart contracts give blockchain the capacity to implement itself once conditions as earlier stipulated are met, hence, eliminating the need for famous middlemen and enhancing the possibility of disputes.
Healthcare:
Blockchain can protect patient’s records by providing privacy as well as sharing records with the relevant healthcare givers. This can help improve patient care and operations in the hospital since tasks are handled efficiently.
Voting Systems:
Such a system can be built using the blockchain, making the elections efficient with no doubt of any kind of manipulation. It can lower the rates of fraud and thus bring back people’s faith in democratic leadership or processes.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Nevertheless, there are challenges that blockchain faces as follows. The scalability also becomes a problem because the program would take a lot of time and resources when processing many transactions. Similarly, diversified regulatory frameworks act as challenges while the energy-consuming process involved in some consensus algorithms such as PoW also acts as a challenge.
Nevertheless, current research work is being concentrated on solving these problems On the same note, research is being done to overcome these difficulties. Solutions such as sharding, the use of layer 2 protocols, and energy-efficient consensus protocols are among the emerging ideas that are steering blockchain networks to new heights of scalability.
Conclusion
One might readily say that blockchain technology belongs to a list of the most groundbreaking technologies in the contemporary world regarding the record, check, or exchange of information. It is uncentralized, sustainable, and safe; hence, it can transform various industries with efficient and better methods. Expanding on this opportunity, one can deduce that the use of such a technology is as diverse as can be when it comes to the furthering of this technology.
Therefore, anyone in this world of tomorrow who is an entrepreneur, a technologist, or an early adopter of technologies must know a little about blockchain.